Condition Assessment
Author: Michael Assadourian, P.E.
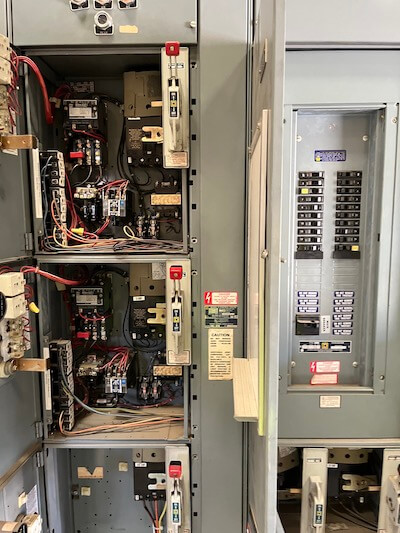


Original construction dates for these facilities range from the early 1970s to 2016, with a few of the older facilities having various rehabilitation improvements projects completed around 2004. Due to the general age of the equipment, some of the Motor Control Centers (MCCs) and Pump Control Panels (PCP) have become difficult to maintain because replacement parts are difficult to find and have the potential to impact reliable operations.
For these reasons, the District‘s Engineering Department initiated the MCCs and PCP Condition Assessment Project and contracted LEE + RO to evaluate the condition of existing motor control equipment within 116 of these facilities located within the District boundaries and within the City of Lake Elsinore.
The main goal is to develop a prioritized list of the Capital Improvement Projects (CIP)s to rehabilitate these facilities.

Besides time and schedule constraints, other challenges facing this project were the large number of facilities to be inspected and tested, and the substantial District region, roughly 40 miles long and 22 miles wide, within which these facilities are scattered. The 116 facilities located within the District boundaries includes:
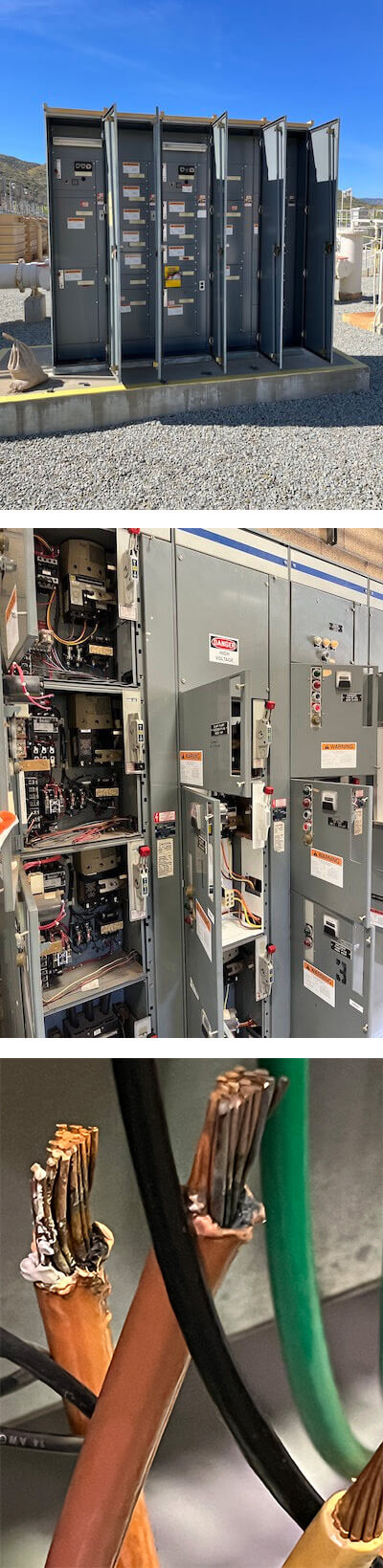

LEE + RO provided professional engineering services for scheduling meetings and coordinating site visits with District staff to allow for visual inspection and evaluation of the 116 facilities. A kick-off meeting was conducted to brainstorm ideas and identify project constraints. To meet the time and schedule constraints LEE + RO:

A site condition assessment was performed at each of the 116 facilities and treatment plants in the City of Elsinore. Site assessments were conducted in conjunction with the testing of the MCCs and PCPs. Detailed photos were taken and organized into a photo set for each of the facilities and included as part of the condition assessment as a separate booklet.
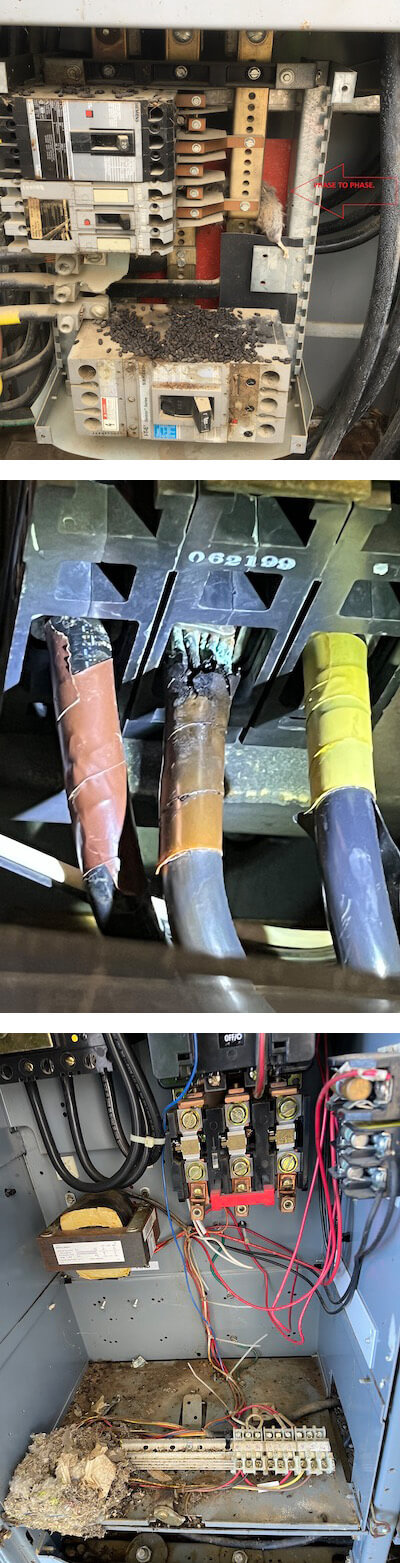

LEE + RO provided a draft and a final copy of the Condition Assessment Report for the District to review. The Report included the following:
The assessment of the District’s Pump Stations was reviewed within three general categories, the Likelihood of Failure (LOF), the Consequence of Failure (COF), and the Risk of Failure. A value scale between 1 to 10 was used to score the LOF and the COF, with 1 as the lowest score and 10 as the highest score. After the values for the LOF and COF were assigned, the Risk of Failure was calculated to determine critical improvements that may require immediate review or mild improvements that could be temporarily delayed in favor of more critical improvements. The Risk of Failure is the overall value of each assessment made. The risk of failure is the product of the LOF and COF.
A high-risk value recommends that this assessment should be reviewed and considered for improvements in the near future. A low-risk value recommends that this assessment could be delayed for improvements in favor for higher risk items. However, a low risk assessment should still be part of daily maintenance and inspections in case of unforeseen events that may progress to a higher risk value.
Based on the analysis and condition assessment, a list of prioritized capital improvement projects (CIP) was developed for all facilities. Project priority was scored based on likelihood and consequence of failure and criticality of the facility.
Lf * Cf * N = P
Lf = Likelihood of Failure (1 – 10, where 10 = most likely)
Cf = Consequence of Failure (1-10, based on various impacts, e.g. unsafe operating condition = 10, etc.)
N = Criticality coefficient (0.0-1.0, with higher scores assigned to the most critical facilities, e.g. older non-renovated)
P = Priority Score (0.0-100, with 100 being the highest priority)
Each facility was assessed electrically in accordance with the test and condition categories listed in the data collection above, and each facility was assigned a total priority score. CIP project sheets were developed for each facility providing necessary information including condition-based defects, recommended project, value added standardization of the facilities, and preliminary cost estimates.